The U.S. economy contracted in the first three months of 2025 on an import surge at the start of President Donald Trump‘s second term in office as he wages a potentially costly trade war.
Gross domestic product, a sum of all the goods and services produced from January through March, fell at a 0.3% annualized pace, according to a Commerce Department report Wednesday adjusted for seasonal factors and inflation. This was the first quarter of negative growth since Q1 of 2022.
Economists surveyed by Dow Jones had been looking for a gain of 0.4% after GDP rose by 2.4% in the fourth quarter of 2024. However, over the past day or so some Wall Street economists changed their outlook to negative growth, largely because of an unexpected rise in imports as companies and consumers sought to get ahead of the Trump tariffs implemented in early April.
Indeed, imports soared 41.3% for the quarter, driven by a 50.9% increase in goods, for the biggest growth outside the Covid pandemic since 1974. Imports subtract from GDP, so the contraction in growth may not be viewed as negatively given the potential for the trend to reverse in subsequent quarters. Imports took more than 5 percentage points off the headline reading. Exports rose 1.8%.
A slowdown in consumer spending and a sharp decline in federal outlays also contributed to the weak GDP number amid Elon Musk’s efforts at the Department of Government Efficiency.
“Maybe some of this negativity is due to a rush to bring in imports before the tariffs go up, but there is simply no way for policy advisors to sugar-coat this. Growth has simply vanished,” said Chris Rupkey, chief economist at Fwdbonds.
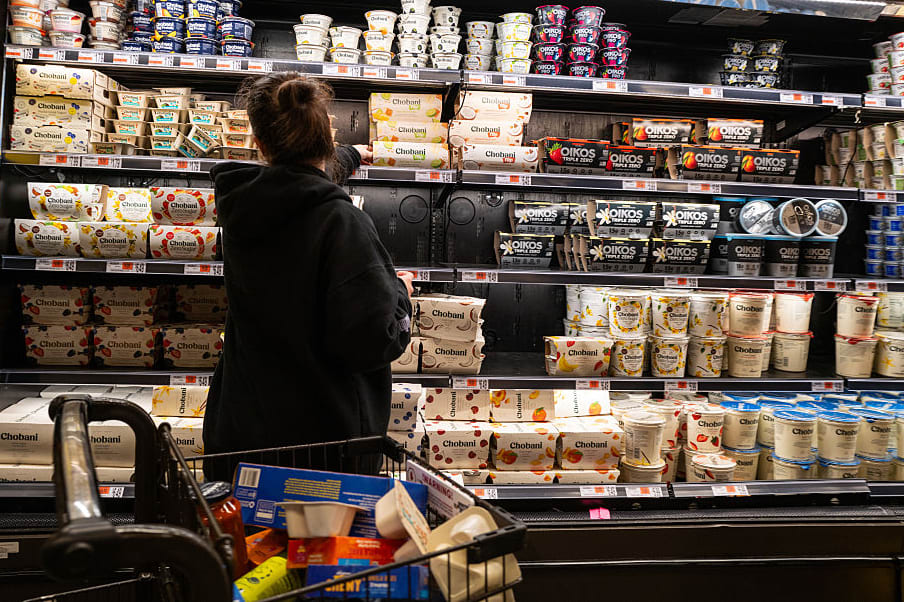
People shop in a Manhattan store on July 27, 2023 in New York City.
Spencer Platt | Getty Images News | Getty Images
Consumer spending slowed during the period but was still positive. Personal consumption expenditures increased 1.8% for the period, the slowest quarterly gain since Q2 of 2023 and down from a 4% gain in the prior quarter. However, a separate report showed that spending was up 0.7% in March, higher than the 0.5% estimate.
Moreover, private domestic investment soared during the period, rising 21.9%, primarily driven by a 22.5% surge in equipment spending that also could have been tariff driven.
Federal government expenditures declined 5.1% for the quarter, shaving about one-third of a percentage point off GDP.
The report comes ahead of the next uncertain steps for Trump’s trade policy.
In early April, the president announced 10% across-the-board tariffs on U.S. trade partners as well as a menu of select “reciprocal” duties against dozens of nations. On April 9, Trump suspended those duties for a 90-day negotiation period that has yet to yield results, though administration officials have indicated that some deals are near.
“No surprise that GDP took a hit in the first quarter, mainly because the balance of trade blew up as companies imported goods like crazy to front-run tariffs. The more telling number for the future of the expansion was consumer spending, and it grew, but at a relatively weak pace,” said Robert Frick, corporate economist with Navy Federal Credit Union. “That’s concerning, but not alarming as it could have been due to bad weather and a spending surge at the end of last year.”
Stock market futures slipped following the report while Treasury yields moved higher.
In a Truth Social post following the report, Trump did not address GDP specifically, instead referring to “Biden’s Stock Market, not Trump’s.”
“Tariffs will soon start kicking in, and companies are starting to move into the USA in record numbers,” Trump wrote. “Our Country will boom, but we have to get rid of the Biden ‘Overhang.’ This will take a while, has NOTHING TO DO WITH TARIFFS, only that he left us with bad numbers, but when the boom begins, it will be like no other. BE PATIENT!!!”
Inflation higher
The report provided cross signals for the Federal Reserve ahead of its policy meeting next week. While the negative growth number might push the central bank to consider lowering interest rates, inflation readings could give policymakers pause.
The personal consumption expenditures price index, the Fed’s preferred inflation measure, posted a 3.6% gain for the quarter, up sharply from the 2.4% increase in Q4. Excluding food and energy, core PCE was up 3.5%. Fed officials consider the core reading a better gauge of long-term trends.
A related reading known as the chain-weighted price index, which adjusts for changes in consumer behavior and other factors, rose 3.7%, well above the 3% estimate.
The Commerce Department reported later in the morning that the PCE price index in March was little changed. The headline annual inflation reading was 2.3% for the month, slightly higher than expected, while core was at 2.6%, as forecast.
Markets still are pricing in a rate cut at the June meeting and a total four moves by the end of the year, a potential indication that the Fed will prioritize economic growth over inflation.
Also Wednesday, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that its employment cost index rose 0.9% in the first quarter, in line with expectations.
While the economy is still adding jobs and consumers are still spending, the GDP report raises both the danger of recession and the stakes for Trump as he negotiates deals with U.S. trading partners.
The traditional rule of thumb for recession is two consecutive negative quarters, though the official arbiter, the National Bureau of Economic Research, uses a definition of “a significant decline in economic activity that is spread across the economy and lasts more than a few months.”
Markets next will look for the BLS nonfarm payrolls data, to be released Friday. Payrolls processing firm ADP reported Wednesday that private hiring rose just 62,000 in April.